You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
<td><a href="https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/how-to-build-a-diy-gnss-reference-station">How to build a DIY GNSS reference station</a></td>
27
27
</tr>
28
28
</table>
29
29
30
30
31
31
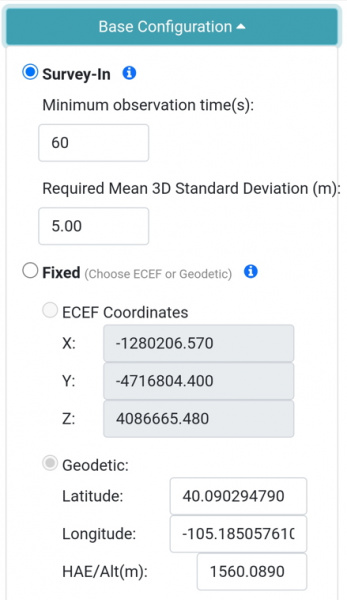
The Base Menu allows the user to select between Survey-In or Fixed Base setups.
32
32
33
-
[](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/1/4/6/3/RTK_Surveyor_-_WiFi_Config_-_Base_Config1.jpg)
33
+

34
34
35
35
*Controlling the type of Base from WiFi AP Config*
36
36
@@ -42,7 +42,13 @@ The Base Menu allows the user to select between Survey-In or Fixed Base setups.
42
42
43
43
In **Survey-In** mode, the minimum observation time and Mean 3D Standard Deviation can be set. The defaults are 60 seconds and 5 meters as directed by u-blox. The device will wait for the position accuracy to be better than 1 meter before a Survey-In is started. Don't be fooled; setting the observation time to 4 hours or an initial positional accuracy of 0.3m is not going to significantly improve the accuracy of the survey - use [PPP](https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/how-to-build-a-diy-gnss-reference-station#gather-raw-gnss-data) instead.
44
44
45
-
In **Fixed** mode, the coordinates of the antenna need to be sent. These can be entered in ECEF or Geographic coordinates. Whenever a user enters Base mode by pressing the SETUP button the GNSS receiver will immediately go into Base mode with these coordinates and immediately begin outputting RTCM correction data.
45
+

46
+
47
+
*Fixed base coordinate input*
48
+
49
+
In **Fixed** mode, the coordinates of the antenna need to be set. These can be entered in ECEF or Geographic coordinates. Whenever a user enters Base mode by pressing the SETUP button the GNSS receiver will immediately go into Base mode with these coordinates and immediately begin outputting RTCM correction data.
50
+
51
+
**Note:** The 'Paste Current XYZ' button will copy the current base coordinates and paste them into the X/Y/Z boxes. This shortcut allows the user to skip writing down coordinates just to re-enter them. However, taking a snap-shot of the unit's position in time is a very inaccurate way to assign the unit's base position.
46
52
47
53
[](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/1/8/5/7/SparkFun_RTK_Express_-_Display_-_Survey-In.jpg)
48
54
@@ -98,6 +104,14 @@ Every second a few hundred bytes, up to ~2k, will be transmitted to your mount p
98
104
99
105
Note: During NTRIP transmission WiFi is turned on and Bluetooth is turned off. You should not need to know the location information of the base so Bluetooth should not be needed. If necessary, USB can be connected to view detailed location information using the [System Report](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/system_status_report/) command.
100
106
107
+
## Commonly Use Coordinates
108
+
109
+

110
+
111
+
*A list of common coordinates*
112
+
113
+
For users who return to the same base position or monument, the coordinates can be saved to a 'Commonly Used Coordinates' list. A nickname and the X/Y/Z positions are saved to the list. Any record on the list can be loaded from the list into the X/Y/Z fields allowing quick switching without the need to hand record or re-enter coordinates from day-to-day repositioning of the base.
114
+
101
115
## Assisted Base
102
116
103
117
An Assisted Base is where a temporary base is set up to Survey-In its location but is simultaneously provided RTCM corrections so that its Survey-In is done with very precise readings. An assisted base running a Survey-In removes much of the relative inaccuracies from a Rover-Base system.
Because of the nature of these controls, the AP config page is different than the terminal menu.
8
8
9
-

9
+

10
10
11
11
*System Config Menu on WiFi AP Config Page*
12
12
13
+
### System Initial State
14
+
15
+
At power on, the device will enter either Rover or Base state.
16
+
13
17
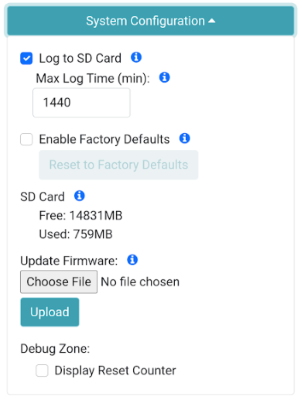
### Log to SD
14
18
15
19
If a microSD card is detected, all messages will be logged.
@@ -22,6 +26,16 @@ Once the max log time is achieved, logging will cease. This is useful for limiti
22
26
23
27
Every 'max long length' amount of time the current log will be closed and a new log will be started. This is known as cyclic logging and is convenient on *very* long surveys (ie, months or years) to prevent logs from getting too unwieldy and helps limit the risk of log corruption. This will continue until the unit is powered down or the *max logging time* is reached.
24
28
29
+
### Start New Log
30
+
31
+
Pressing the 'Start New Log' button will close the current log. A new log will be opened when the AP Config page is closed and the unit restarts. This can be helpful in the field when a certain set of coordinates or feature marks need to be recorded in close proximity to one another. By dividing up the logs, the work can be more easily identified.
32
+
33
+
### Bluetooth Protocol
34
+
35
+
By default, the RTK products use Bluetooth v2.0 SPP (Serial Port Profile) to connect to data collectors. Nearly all data collectors support this protocol. The RTK product line also supports BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy). The BLE protocol has a variety of improvements but very few data collectors support it.
36
+
37
+
**Note:** Bluetooth SPP cannot operate concurrently with ESP-Now radio transmissions. Therefore, if you plan to use the ESP-Now radio system to connect RTK products, the BLE protocol must be used to communicate over Bluetooth to data collectors. Alternatively, ESP-Now works concurrently with WiFi so connecting to a data collector over WiFi can be used.
38
+
25
39
### Enable Factory Defaults
26
40
27
41
Factory Defaults will erase any user settings and reset the internal receiver to stock settings. Any logs on SD are maintained. To prevent accidental reset the checkbox must first be checked before the button is pressed.
@@ -32,11 +46,11 @@ Various stats for the SD card are shown.
32
46
33
47
### Update Firmware
34
48
35
-
New firmware may be uploaded via WiFi to the unit. See [Updating Firmware from the SD Card](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/firmware_update/#updating-firmware-from-the-sd-card) for more information.
49
+
New firmware may be uploaded via WiFi to the unit. See [Updating Firmware from WiFi](https://docs.sparkfun.com/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/firmware_update/#updating-firmware-from-wifi) for more information.
36
50
37
51
### Reset Counter
38
52
39
-
A counter is displayed indicating the number of non-power-on-resets since the last poweron.
53
+
A counter is displayed indicating the number of non-power-on-resets since the last power-on.

6
+
7
+
*Configuration page via WiFi*
8
+
5
9
Starting with firmware v1.7, WiFi-based configuration is supported. For more information about updating the firmware on your device, please see [Updating RTK Firmware](https://sparkfun.github.io/SparkFun_RTK_Firmware/firmware_update/).
6
10
7
11
The RTK device will present a webpage that is viewable from either a desktop/laptop with WiFi or a cell phone. For advanced configurations, a desktop is recommended. For quick in-field changes, a cell phone works great.
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: docs/firmware_update.md
+1-1Lines changed: 1 addition & 1 deletion
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ In the rare event that a unit is not staying on long enough for new firmware to
76
76
77
77
**Note:** Firmware versions 1.1 to 1.9 have an issue that severely limits firmware upload over WiFi and is not recommended; use the 'Updating Firmware From Windows GUI' method instead. Firmware versions v1.10 and beyond support direct firmware updates via WiFi.
78
78
79
-
[](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/learn_tutorials/2/1/8/8/SparkFun_RTK_Facet_-_WiFi_Config_Firmware_Update_Button.jpg)
79
+

0 commit comments