|
1 | | -Programming ATtiny84x in Circuit |
| 1 | +Programming SAMD21 in Circuit |
2 | 2 | =========================================================== |
3 | 3 |
|
4 | | -The Qwiic Twist uses an ATtiny84A that must be programmed with firmware. This is done with spring pins aka Pogo Pins and an AVR programmer of your choice. We've had success with using an [Arduino as the ISP programmer](https://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/BuiltInExamples/ArduinoISP) but we use the [Tiny AVR Programmer](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/11801) for day to day work. |
5 | | - |
6 | | -1) Get the Tiny AVR Programmer and the [necessary drivers](https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/tiny-avr-programmer-hookup-guide#driver-installation) installed. |
7 | | -2) Clear the VCC solder jumper from the Tiny AVR Programmer. This jumper is closed by default and will power the target at 5V. While 5V will not harm the ATtiny targets, but many Qwiic boards have 3.3V sensitive sensors and peripherals so it's best to power the target through a Qwiic cable. |
8 | | -3) Solder 6-pin [female header](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/115) to the bottom of the programmer |
9 | | -4) Assemble the [SparkFun ISP Pogo Adapter](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/11591) |
10 | | -5) Attach the pogo adapter to the bottom of the programmer. |
11 | | - |
12 | | - |
13 | | - |
14 | | - |
15 | | -6) Identify and mark pin 1 on the bottom of the adapter. You'll need to know where pin 1 is to align it on the target ISP holes. |
16 | | - |
17 | | - |
18 | | - |
19 | | -7) Attach Tiny AVR Programmer to a USB extension cable to allow free movement of the programmer. Confirm that avrdude can see the programmer. |
20 | | -8) Connect the target device to a development board using a Qwiic cable so that it is powered. |
21 | | -9) Download the contents of the 'Programming' folder so that you have **avrdude.exe**, **avrdude.conf**, and **program_qwiic_twist.bat** in a folder. |
22 | | -9) Open a command line, navigate to 'program_qwiic_twist.bat' and run. It should fail because no ATtiny was detected. If it failed because an attinyusb was not found then you may need to troubleshoot your Tiny AVR Programmer and/or edit the batch file to match your programmer type. |
23 | | -10) Press and hold the pogo pins against the 6 exposed pins on the target. Your mark on the pogo pins should match with the small white silkscreen on the ISP on the target. You may need to wiggle the Pogo adapter until you hear all 6 pins seat into the ISP footprint. |
24 | | - |
25 | | -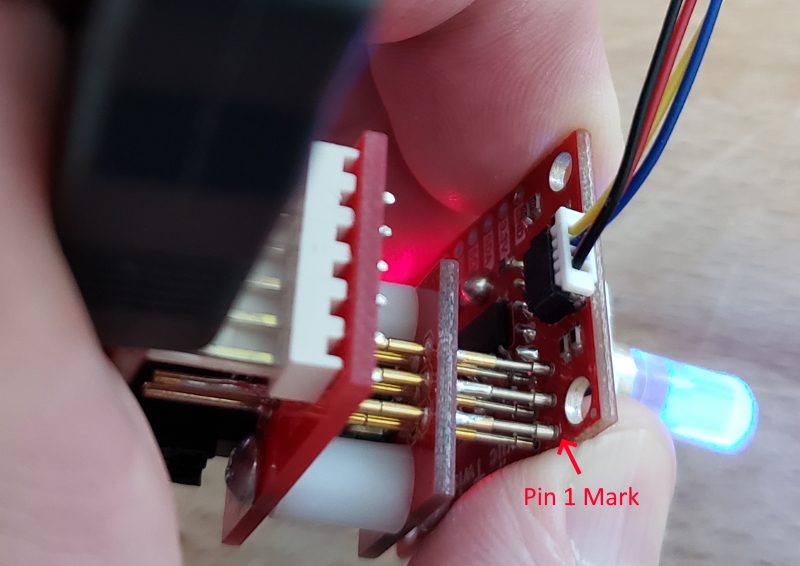 |
26 | | - |
27 | | - |
28 | | -11) Press enter with your free hand to begin programming. |
29 | | - |
| 4 | +LoRaSerial uses a SAMD21. This folder contains the various production and release binaries for the device. Please see [Updating LoRaSerial Firmware](https://docs.sparkfun.com/SparkFun_LoRaSerial/firmware_update/) for instructions on how to update the firmware on the device. |
30 | 5 |
|
| 6 | +This folder also contains binaries combined with a UF2 bootloader. These binaries are loaded during production to allow both the bootloader and firmware to be loaded in one step. These files, along with atprogram.exe are used with a J-Link programmer to load the combined binary onto a target device. |
0 commit comments