|
| 1 | +Sure! Here's the full `README.md` in the LeetCode-style format, exactly like in the `doocs/leetcode` GitHub repo, for **1372. Longest ZigZag Path in a Binary Tree**: |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +--- |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +```markdown |
| 6 | +# [1372. Longest ZigZag Path in a Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-zigzag-path-in-a-binary-tree) |
| 7 | + |
| 8 | +## Description |
| 9 | + |
| 10 | +You are given the `root` of a binary tree. |
| 11 | + |
| 12 | +A ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follows: |
| 13 | + |
| 14 | +- Choose **any** node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left). |
| 15 | +- If the current direction is right, move to the right child of the current node; otherwise, move to the left child. |
| 16 | +- Change the direction from right to left or from left to right. |
| 17 | +- Repeat the second and third steps until you can't move in the tree. |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +The ZigZag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0). |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +Return _the longest **ZigZag** path contained in that tree_. |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +## Examples |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +**Example 1:** |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +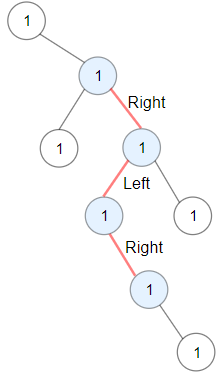 |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +``` |
| 30 | +Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1] |
| 31 | +Output: 3 |
| 32 | +Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right). |
| 33 | +``` |
| 34 | +
|
| 35 | +**Example 2:** |
| 36 | +
|
| 37 | +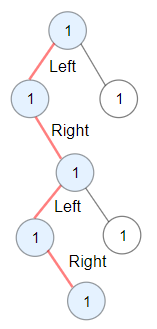 |
| 38 | +
|
| 39 | +``` |
| 40 | +Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1] |
| 41 | +Output: 4 |
| 42 | +Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right). |
| 43 | +``` |
| 44 | +
|
| 45 | +**Example 3:** |
| 46 | +
|
| 47 | +``` |
| 48 | +Input: root = [1] |
| 49 | +Output: 0 |
| 50 | +``` |
| 51 | +
|
| 52 | +## Constraints |
| 53 | +
|
| 54 | +- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[1, 5 * 10^4]`. |
| 55 | +- `1 <= Node.val <= 100` |
| 56 | +
|
| 57 | +## Solutions |
| 58 | +
|
| 59 | +### Python3 |
| 60 | +
|
| 61 | +```python |
| 62 | +# Definition for a binary tree node. |
| 63 | +# class TreeNode: |
| 64 | +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): |
| 65 | +# self.val = val |
| 66 | +# self.left = left |
| 67 | +# self.right = right |
| 68 | +class Solution: |
| 69 | + def longestZigZag(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: |
| 70 | + def dfs(root, l, r): |
| 71 | + if root is None: |
| 72 | + return |
| 73 | + nonlocal ans |
| 74 | + ans = max(ans, l, r) |
| 75 | + dfs(root.left, r + 1, 0) |
| 76 | + dfs(root.right, 0, l + 1) |
| 77 | +
|
| 78 | + ans = 0 |
| 79 | + dfs(root, 0, 0) |
| 80 | + return ans |
| 81 | +``` |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | +### Java |
| 84 | + |
| 85 | +```java |
| 86 | +/** |
| 87 | + * Definition for a binary tree node. |
| 88 | + * public class TreeNode { |
| 89 | + * int val; |
| 90 | + * TreeNode left; |
| 91 | + * TreeNode right; |
| 92 | + * TreeNode() {} |
| 93 | + * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } |
| 94 | + * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { |
| 95 | + * this.val = val; |
| 96 | + * this.left = left; |
| 97 | + * this.right = right; |
| 98 | + * } |
| 99 | + * } |
| 100 | + */ |
| 101 | +class Solution { |
| 102 | + private int ans; |
| 103 | + |
| 104 | + public int longestZigZag(TreeNode root) { |
| 105 | + dfs(root, 0, 0); |
| 106 | + return ans; |
| 107 | + } |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | + private void dfs(TreeNode root, int l, int r) { |
| 110 | + if (root == null) { |
| 111 | + return; |
| 112 | + } |
| 113 | + ans = Math.max(ans, Math.max(l, r)); |
| 114 | + dfs(root.left, r + 1, 0); |
| 115 | + dfs(root.right, 0, l + 1); |
| 116 | + } |
| 117 | +} |
| 118 | +``` |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | +### C++ |
| 121 | + |
| 122 | +```cpp |
| 123 | +/** |
| 124 | + * Definition for a binary tree node. |
| 125 | + * struct TreeNode { |
| 126 | + * int val; |
| 127 | + * TreeNode *left; |
| 128 | + * TreeNode *right; |
| 129 | + * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} |
| 130 | + * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} |
| 131 | + * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} |
| 132 | + * }; |
| 133 | + */ |
| 134 | +class Solution { |
| 135 | +public: |
| 136 | + int ans = 0; |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | + int longestZigZag(TreeNode* root) { |
| 139 | + dfs(root, 0, 0); |
| 140 | + return ans; |
| 141 | + } |
| 142 | + |
| 143 | + void dfs(TreeNode* root, int l, int r) { |
| 144 | + if (!root) return; |
| 145 | + ans = max(ans, max(l, r)); |
| 146 | + dfs(root->left, r + 1, 0); |
| 147 | + dfs(root->right, 0, l + 1); |
| 148 | + } |
| 149 | +}; |
| 150 | +``` |
| 151 | +
|
| 152 | +### Go |
| 153 | +
|
| 154 | +```go |
| 155 | +/** |
| 156 | + * Definition for a binary tree node. |
| 157 | + * type TreeNode struct { |
| 158 | + * Val int |
| 159 | + * Left *TreeNode |
| 160 | + * Right *TreeNode |
| 161 | + * } |
| 162 | + */ |
| 163 | +func longestZigZag(root *TreeNode) int { |
| 164 | + ans := 0 |
| 165 | + var dfs func(root *TreeNode, l, r int) |
| 166 | + dfs = func(root *TreeNode, l, r int) { |
| 167 | + if root == nil { |
| 168 | + return |
| 169 | + } |
| 170 | + ans = max(ans, max(l, r)) |
| 171 | + dfs(root.Left, r+1, 0) |
| 172 | + dfs(root.Right, 0, l+1) |
| 173 | + } |
| 174 | + dfs(root, 0, 0) |
| 175 | + return ans |
| 176 | +} |
| 177 | +
|
| 178 | +func max(a, b int) int { |
| 179 | + if a > b { |
| 180 | + return a |
| 181 | + } |
| 182 | + return b |
| 183 | +} |
| 184 | +``` |
| 185 | + |
| 186 | +--- |
| 187 | + |
| 188 | +Let me know if you want this in other languages or with a visual diagram too! |
0 commit comments