|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +Title: '.axis()' |
| 3 | +Description: 'Gets or sets the properties of the plot axes, including axis limits, scaling, and visibility.' |
| 4 | +Subjects: |
| 5 | + - 'Computer Science' |
| 6 | + - 'Data Science' |
| 7 | + - 'Data Visualization' |
| 8 | +Tags: |
| 9 | + - 'Data' |
| 10 | + - 'Graphs' |
| 11 | + - 'Libraries' |
| 12 | + - 'Matplotlib' |
| 13 | + - 'Plotting' |
| 14 | +CatalogContent: |
| 15 | + - 'learn-python-3' |
| 16 | + - 'paths/computer-science' |
| 17 | +--- |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +The **`.axis()`** function in Matplotlib's [`pyplot`](https://www.codecademy.com/resources/docs/matplotlib/pyplot) module gets or sets properties of the plot axes, including axis limits, aspect ratio, and visibility. |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +## Syntax |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +```pseudo |
| 24 | +matplotlib.pyplot.axis(arg=None, emit=True, **kwargs) |
| 25 | +``` |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +The function can be called in several ways: |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +- `axis()`: Returns current axis limits as `(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)` |
| 30 | +- `axis([xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax])`: Sets axis limits |
| 31 | +- `axis(option)`: Sets axis properties using predefined options |
| 32 | +- `axis(**kwargs)`: Sets axis properties using keyword arguments |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +**Parameters:** |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +- `arg` (optional): Defines how the axes are set or displayed. Accepts the following values: |
| 37 | + - A list or tuple `[xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]` to set axis limits. |
| 38 | + - `'off'` to hide the axes. |
| 39 | + - `'on'` to show the axes. |
| 40 | + - `'equal'`, `'scaled'`, `'tight'`, `'auto'`, `'image'`, `'square'` — control axis scaling and aspect ratio. |
| 41 | +- `emit` (bool, default: True): If `True`, notifies observers of axis limit changes. |
| 42 | +- `kwargs` (optional): Additional axis properties such as `xmin`, `xmax`, `ymin`, and `ymax`. |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | +**Return value:** |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | +Returns a [tuple](https://www.codecademy.com/resources/docs/python/tuples) `(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)` representing the current axis limits. |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +## Example 1: Using `.axis()` to Control Axis Properties |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +This example creates three subplots demonstrating different axis control modes. The first subplot uses `axis([2, 8, -0.5, 0.5])` to restrict the view to specific x and y ranges. The second subplot uses `axis('equal')` to ensure both axes use the same scale. The third subplot uses `axis('off')` to hide the axis lines, ticks, and labels: |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +```py |
| 53 | +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
| 54 | +import numpy as np |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +# Generate sample data |
| 57 | +x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100) |
| 58 | +y = np.sin(x) |
| 59 | + |
| 60 | +# Create a basic plot |
| 61 | +plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4)) |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | +# Subplot 1: Custom axis limits |
| 64 | +plt.subplot(1, 3, 1) |
| 65 | +plt.plot(x, y) |
| 66 | +plt.axis([2, 8, -0.5, 0.5]) |
| 67 | +plt.title('Custom Limits') |
| 68 | +plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3) |
| 69 | + |
| 70 | +# Subplot 2: Equal aspect ratio |
| 71 | +plt.subplot(1, 3, 2) |
| 72 | +plt.plot(x, y) |
| 73 | +plt.axis('equal') |
| 74 | +plt.title('Equal Scaling') |
| 75 | +plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3) |
| 76 | + |
| 77 | +# Subplot 3: Axis turned off |
| 78 | +plt.subplot(1, 3, 3) |
| 79 | +plt.plot(x, y) |
| 80 | +plt.axis('off') |
| 81 | +plt.title('Hidden Axes') |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | +plt.tight_layout() |
| 84 | +plt.show() |
| 85 | +``` |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | +The output of this code is: |
| 88 | + |
| 89 | +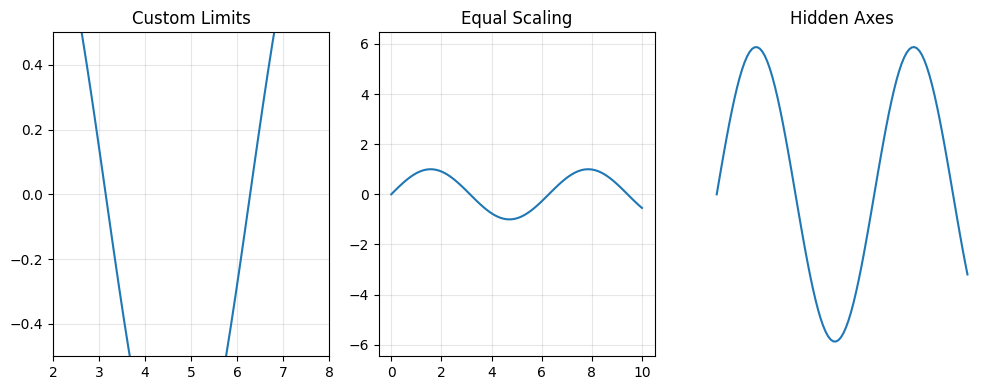 |
| 90 | + |
| 91 | +## Example 2: Getting and Setting Axis Limits |
| 92 | + |
| 93 | +This example demonstrates how to set custom axis limits and retrieve the current limits. The `axis()` function is called with a list of four values to set the x and y axis ranges, then called without arguments to return the current limits as a tuple. |
| 94 | + |
| 95 | +```py |
| 96 | +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
| 97 | +import numpy as np |
| 98 | + |
| 99 | +# Create data |
| 100 | +x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100) |
| 101 | +y = np.sin(x) |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | +# Create plot |
| 104 | +plt.plot(x, y, linewidth=2) |
| 105 | +plt.title('Sine Wave with Custom Axes') |
| 106 | + |
| 107 | +# Set custom axis limits |
| 108 | +plt.axis([0, 2*np.pi, -1.5, 1.5]) |
| 109 | + |
| 110 | +# Get and print current axis limits |
| 111 | +limits = plt.axis() |
| 112 | +print(f"Current axis limits: {limits}") |
| 113 | + |
| 114 | +plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3) |
| 115 | +plt.show() |
| 116 | +``` |
| 117 | + |
| 118 | +The output of this code is: |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | +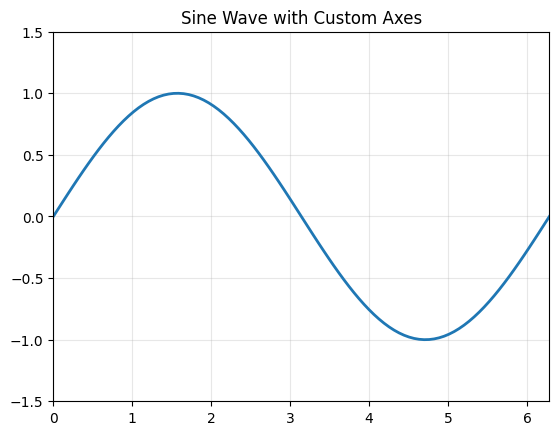 |
0 commit comments