|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +Title: '.stackplot()' |
| 3 | +Description: 'Creates a stacked area plot to show how multiple datasets contribute cumulatively over time or categories.' |
| 4 | +Subjects: |
| 5 | + - 'Data Science' |
| 6 | + - 'Data Visualization' |
| 7 | +Tags: |
| 8 | + - 'Charts' |
| 9 | + - 'Matplotlib' |
| 10 | + - 'Stacks' |
| 11 | +CatalogContent: |
| 12 | + - 'learn-python-3' |
| 13 | + - 'paths/data-science' |
| 14 | +--- |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | +The **`.stackplot()`** method in Matplotlib creates stacked area plots (also known as stacked area charts) that display multiple datasets as vertically stacked areas. Each area represents the cumulative contribution of different categories to a total, making it ideal for visualizing proportional relationships as those relationships change over time. |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +## Syntax |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +```pseudo |
| 21 | +matplotlib.pyplot.stackplot(x, *args, labels=(), colors=None, hatch=None, baseline='zero', data=None, **kwargs) |
| 22 | +``` |
| 23 | + |
| 24 | +**Parameters:** |
| 25 | + |
| 26 | +- `x`: Array-like. The x-coordinates of the data points. |
| 27 | +- `*args`: One or more array-like sequences representing the y-values for each stack layer. |
| 28 | +- `labels`: List of strings, optional. Labels for each stack layer (used in legends). |
| 29 | +- `colors`: List of colors or color specifications for each stack layer. |
| 30 | +- `hatch`: String or sequence, optional. Hatching patterns applied to the filled areas. |
| 31 | +- `baseline`: String, defines the baseline for stacking: |
| 32 | + - `'zero'` (default): Stack from y = 0. |
| 33 | + - `'sym'`: Symmetric stacking around zero. |
| 34 | + - `'wiggle'`: Minimizes slope changes between layers. |
| 35 | + - `'weighted_wiggle'`: Weighted version of the wiggle baseline. |
| 36 | +- `data`: Object with labeled data (e.g., dict or DataFrame). Optional data source. |
| 37 | +- `**kwargs`: Additional keyword arguments passed to `PolyCollection` (e.g., `alpha` for transparency). |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +**Return value:** |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | +Returns a list of `PolyCollection` objects, one for each stack layer. |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +## Example 1: Visualizing Monthly Sales by Category |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +This example shows a stacked area chart of sales data across product categories over time: |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | +```py |
| 48 | +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +# Sample data |
| 51 | +months = ['Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar', 'Apr', 'May', 'Jun'] |
| 52 | +electronics = [20, 25, 30, 28, 35, 40] |
| 53 | +clothing = [15, 18, 22, 25, 20, 30] |
| 54 | +books = [10, 12, 15, 18, 22, 25] |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +# Create stacked area plot |
| 57 | +plt.stackplot(months, electronics, clothing, books, |
| 58 | + labels=['Electronics', 'Clothing', 'Books'], |
| 59 | + colors=['#ff9999', '#66b3ff', '#99ff99'], |
| 60 | + alpha=0.8) |
| 61 | + |
| 62 | +plt.xlabel('Month') |
| 63 | +plt.ylabel('Sales (in thousands)') |
| 64 | +plt.title('Monthly Sales by Category') |
| 65 | +plt.legend(loc='upper left') |
| 66 | +plt.show() |
| 67 | +``` |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +This creates a stacked area chart where each colored area represents a product category's contribution to total sales: |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +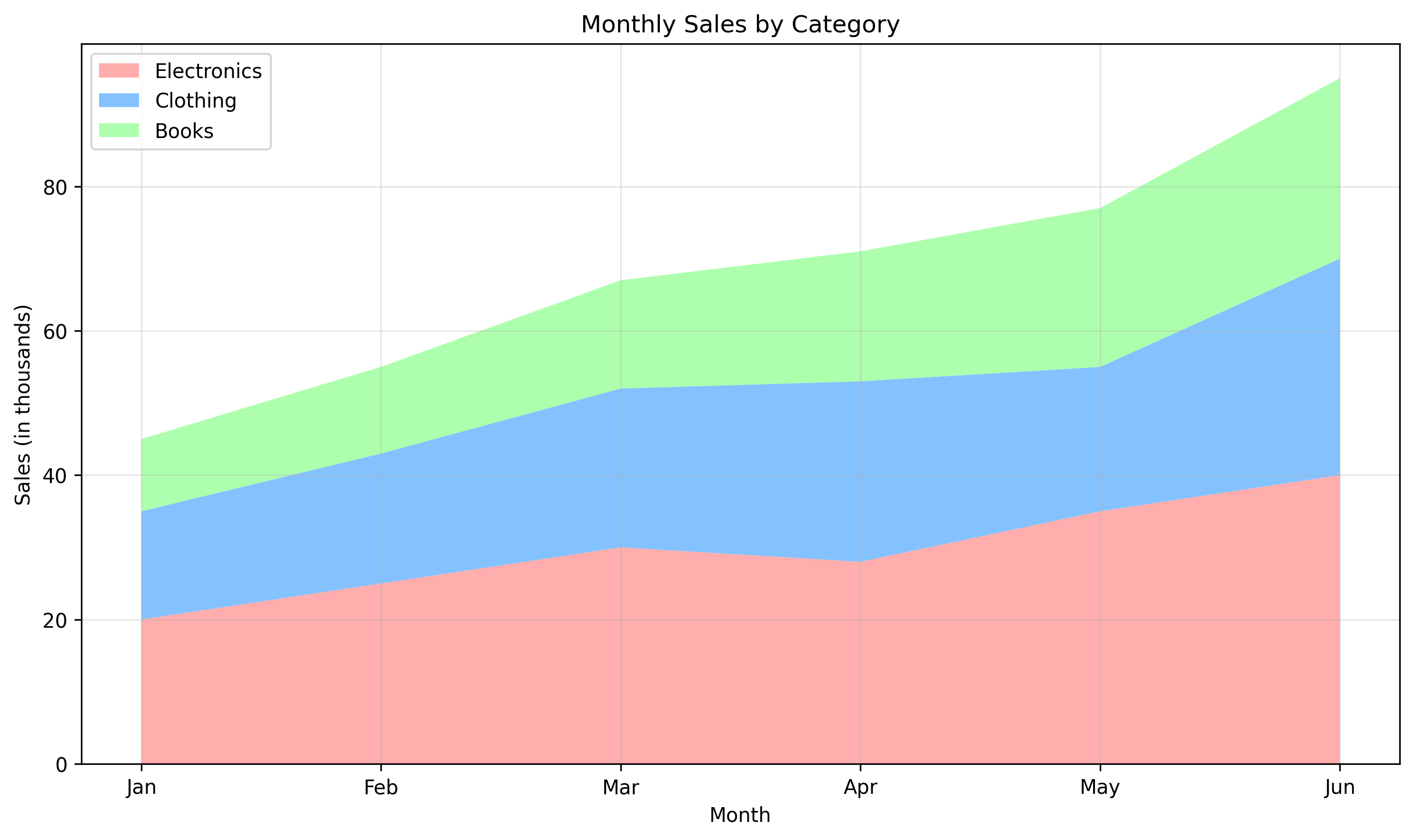 |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +## Example 2: Stacked Areas with Multiple Series |
| 74 | + |
| 75 | +This example demonstrates stacking multiple data series using numeric values: |
| 76 | + |
| 77 | +```py |
| 78 | +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
| 79 | +import numpy as np |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | +# Create sample data |
| 82 | +x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] |
| 83 | +y1 = [1, 2, 3, 2, 1] |
| 84 | +y2 = [2, 3, 2, 4, 3] |
| 85 | +y3 = [1, 1, 2, 1, 2] |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | +# Create stackplot |
| 88 | +plt.stackplot(x, y1, y2, y3, |
| 89 | + labels=['Series A', 'Series B', 'Series C'], |
| 90 | + colors=['lightcoral', 'lightblue', 'lightgreen'], |
| 91 | + alpha=0.8) |
| 92 | + |
| 93 | +plt.xlabel('X Values') |
| 94 | +plt.ylabel('Y Values') |
| 95 | +plt.title('Basic Stackplot Example') |
| 96 | +plt.legend(loc='upper left') |
| 97 | +plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3) |
| 98 | +plt.show() |
| 99 | +``` |
| 100 | + |
| 101 | +This creates a basic stacked area plot with three data series, demonstrating the fundamental structure of stackplot visualizations: |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | +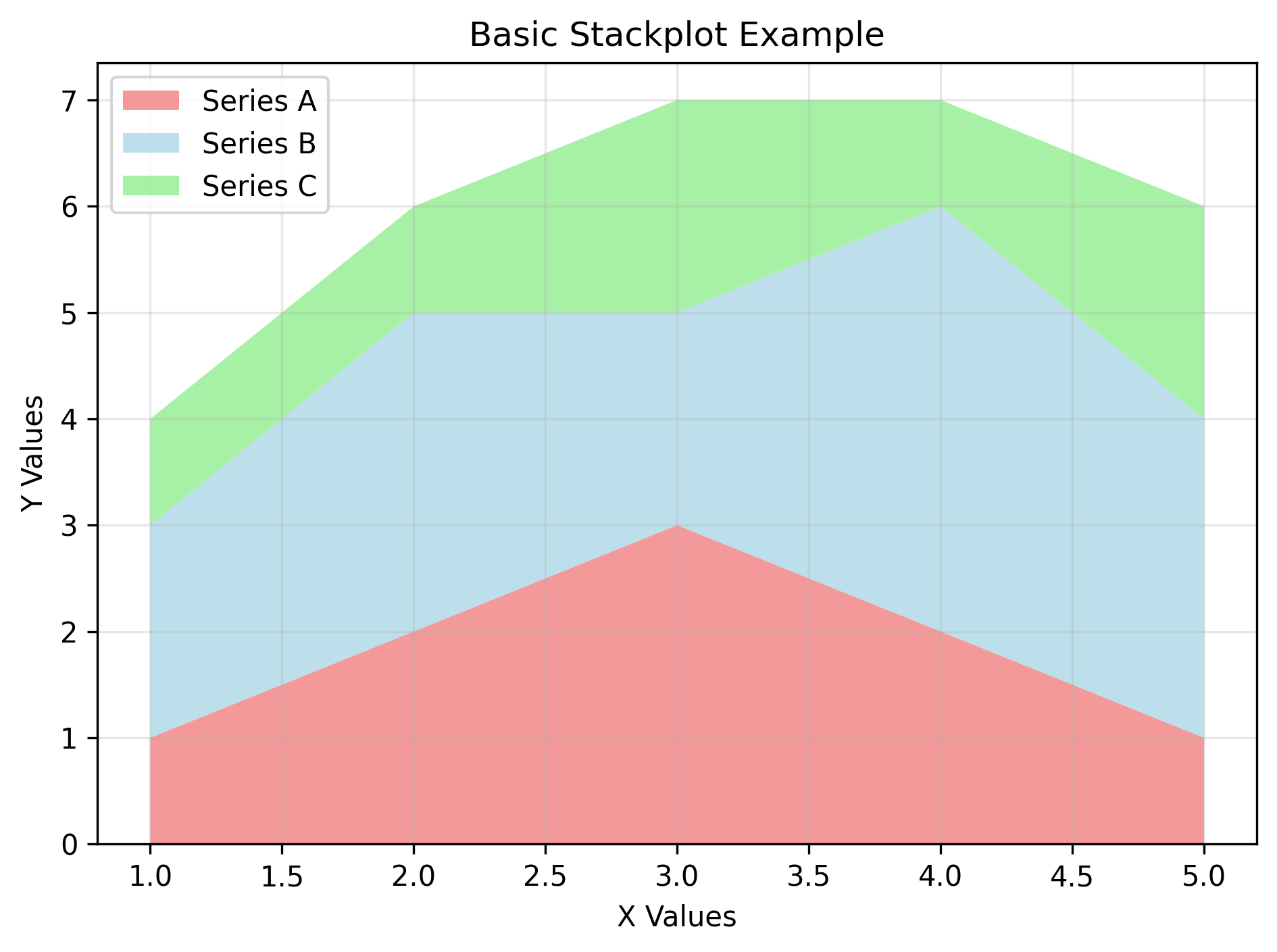 |
0 commit comments